- Dubai’s used-car market at a glance
- Where to find used cars in Dubai
- Set a realistic budget (total cost of ownership) Consider:
- Pre-purchase checklist and inspection
- Documents to verify before paying
- How to negotiate and place a deposit safely
- Insurance and financing basics
- Exporting a car from Dubai
- Common scams and red flags
Looking to buy a car in Dubai without overpaying or risking hidden faults? This step-by-step guide covers where to find the best deals, what to check before you pay, how RTA transfer works, insurance and financing basics, and how to avoid scams. Whether you’re shopping for used cars in Dubai from certified dealers or private sellers, or considering second-hand cars in Dubai for export, you’ll find everything you need here.
Dubai’s used-car market at a glance
Competitive market: High car turnover, many expats, corporate fleets, and dealer trade-ins mean strong supply of second hand cars in Dubai. Age and mileage: Many cars are well-maintained and relatively new. Still, always verify service history. Specs matter: GCC-spec vehicles are generally preferred for local climate; non‑GCC (e.g., US import) can be fine if properly repaired and documented.
Where to find used cars in Dubai
Online marketplaces: Popular platforms list thousands of used cars in Dubai with filters for year, mileage, specs, and service history. Certified dealers: “Approved” or “certified pre-owned” showrooms offer inspected cars, limited warranties, and easier financing. Large multi-brand showrooms and auto markets: Areas like Ras Al Khor/Al Aweer Auto Market have extensive inventories you can compare in one trip. Auction and fleet sales: Potential bargains, but inspect thoroughly and know the fee structure. Word of mouth/company fleets: Corporate disposals can be well-maintained with full history.
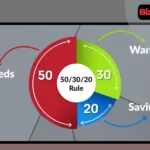
Set a realistic budget (total cost of ownership) Consider:
- Purchase price
- Registration and testing fees
- Insurance (third-party vs comprehensive)
- Possible dealer/admin fees and, where applicable, VAT
- Loan down payment (commonly around 20%) and monthly installments
- Maintenance, tires, battery, and unexpected repairs
- Salik (toll), parking, fuel Tip: Price similar used cars in Dubai by year, trim, mileage, and service history to set your offer range.
Pre-purchase checklist and inspection
- Service history: Prefer stamped dealer/service-book or digital records. Cross-check mileage consistency.
- Accident and chassis: Look for overspray, uneven panel gaps, weld marks, and rust. Ask for any body-shop reports.
- Mechanical: Engine idle smoothness, cold start, leaks, cooling system efficiency (AC must blow very cold), transmission shifts, suspension noises, brakes vibration.
- Electrical and features: Infotainment, cameras/sensors, ADAS, sunroof, windows, lights, keyless entry.
- Tires and brakes: Check tread depth and even wear; mismatch may indicate prior issues.
- GCC vs non‑GCC: Confirm radiator size, AC condenser, and cooling upgrades for hot weather if non‑GCC.
- Professional inspection: Use an independent workshop or a recognized testing center to get a full report.
- RTA/Tasjeel test: For older vehicles, a recent pass is useful evidence the car is roadworthy.
Documents to verify before paying
- Mulkiya (registration card): Confirm owner’s name, VIN, plate, and expiry.
- Emirates ID/passport copy (seller): Matches the registered owner.
- Loan status: Ensure there’s no active “mortgage” (bank lien). If present, seller must settle and obtain a mortgage release before transfer.
- Service records and invoices: Prefer originals or verifiable digital logs.
- Spare keys, manuals, accessories: Note any missing items to adjust price.
- Police/RTA fines: Must be cleared before transfer.
How to negotiate and place a deposit safely
- Know market value: Compare at least 5–10 comparable listings for second hand cars in Dubai with similar trim and mileage.
- Use inspection results: Quote required repairs to justify a lower offer.
- Be ready to walk away: There are plenty of options.
- Deposit best practices:
- Use a simple written agreement stating price, refundable conditions, and timeline to complete RTA transfer.
- Avoid large cash deposits; use traceable payment.
- Never leave your original ID with the seller.
Ownership transfer (RTA/Tasjeel) step-by-step Note: Processes are streamlined at authorized centers (e.g., Tasjeel/Shamil/Wasel). Exact fees and steps can vary by vehicle type and policy updates, but the flow is generally:
- Clear liabilities
- Seller settles outstanding fines, Salik dues, and any bank mortgage (obtain mortgage release).
- Insurance
- Buyer arranges at least third-party insurance (policy must be active for registration).
- Technical testing (if required)
- Vehicles beyond a certain age require a passing roadworthiness test; many centers can do test + transfer on-site.
- Documents you’ll need
- Buyer: Emirates ID, UAE driving license, valid insurance.
- Seller: Emirates ID and original Mulkiya.
- Both parties (or authorized representatives) usually attend the counter together.
- Transfer and plates
- The center issues the new Mulkiya in the buyer’s name.
- Plate handling: Keep existing plates or purchase new ones depending on preference and rules.
- Pay fees
- Transfer, knowledge/innovation, testing (if any), and plate fees. Keep all receipts.
Insurance and financing basics
- Insurance
- Third-party is mandatory; comprehensive gives better protection for newer or higher-value cars.
- Compare at least 3 quotes; factors include driver age, claims history, car value, and repair type (agency vs non-agency).
- Add-ons: GCC cover, roadside assistance, personal accident, hire car benefit.
- Financing
- Many banks and dealers offer auto loans to residents; typical down payment around 20% with tenures up to 60 months, subject to income and credit checks.
- Ensure the valuation used by the bank matches the agreed price to avoid shortfalls.
- Watch for processing fees and early settlement charges.
Exporting a car from Dubai
- Obtain an export certificate at an authorized center.
- Arrange export plates and export insurance for transport.
- Clear any loans/fines before export.
- Confirm destination country’s import rules, duties, and compliance (e.g., emissions, left/right-hand drive).
Common scams and red flags
- “Just imported, low price”: Verify accident history; look for flood or salvage repair indicators.
- Odometer tampering: Cross-check mileage across service records and onboard diagnostics.
- Curbstoners: Unlicensed sellers posing as private owners. Ask to meet at registration address and verify ID.
- Pressure tactics: “Another buyer is coming in 10 minutes.” Take your time and insist on inspection.
- Incomplete documents: Never pay in full until all documents and liabilities are confirmed.